A Linked Service in Azure
Data Factory (ADF) is a reference to a data store or a compute
service. Think of it as a connection string that ADF uses to securely connect
to external resources. Linked Services are essential for specifying how ADF
should connect to various sources and destinations of data, as well as
computing environments for data processing.
What is ADF
Linked Service?
Definition: Linked service defines the connection
information to a data store or Azure compute service.
- ADF
primarily is an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool (Extract, Transform and
Load). So obviously, we need to connect to data sources to work on it.
- The
activities in the ADF pipeline are the actions to be performed on your data.
But the question is how do we connect to the data source from the ADF pipeline?
The answer is using ADF Linked Service.
- A few examples:
- Example 1: You want to copy some files from SharePoint to Azure BLOB
storage. In this case you will require two separate Linked Services. One to
connect with SharePoint database (Your Source) and one to connect to Azure BLOB
Storage (your destination).
- Example 2: You want to execute a stored procedure on Azure SQL
Database. To connect to Azure SQL DB, you need to create an ADF Linked Service.
How to implement
parameterized Linked Service in ADF?
- You can have parameters in the linked service so
that when you use them in your dataset, you can use dynamic values.
- It is recommended not to parameterize the
username, password or any other such sensitive information.
- There is an open bug to use "-" in
parameter names, it is recommended to use names without "-" until
the bug is resolved.
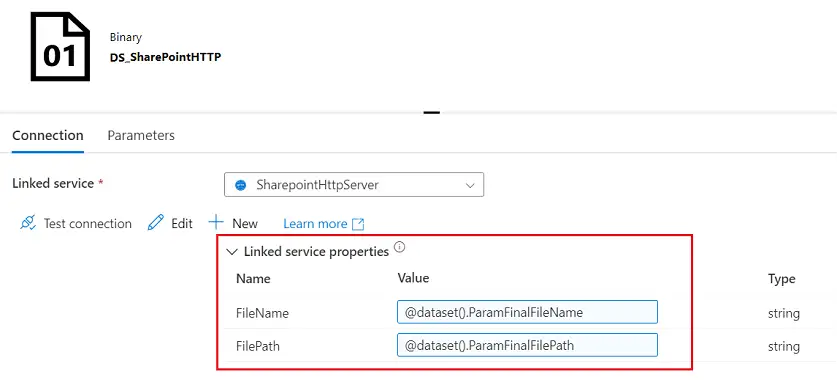
- Example:
- Here, we have created an HTTP Linked Service for
SharePoint connection. Using this we are trying to get to the file residing in
a SharePoint document library.
- Now we are going to pass two parameters here. As
you can see in the screenshot, we can also provide the default values.
- FileName
- FilePath
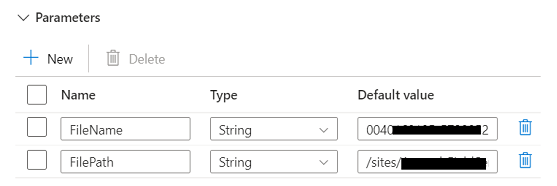
- We will now open the dataset where we have used
this Linked Service. In the connection tab, you can expand the parameters
option. As shown in the screenshot, the two parameters’ values are provided
dynamically using the pipeline variables.
Example 1: How
to create an ADF Linked service to Azure SQL?
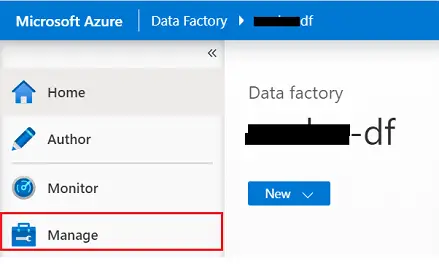
- Go to Azure Portal
- Go to your ADF resource.
- From the top left section, click on Manage.
- Now, click on New and then search for Azure
SQL Database. Select the Data store and click on continue

- Configure the connection details.
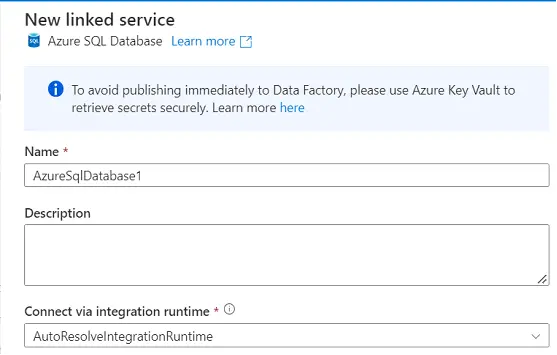
- Name: Give a meaningful name to your
Linked Service.
- Description: Describe your Linked service
in a few understandable words.
- Connect via integration runtime: The
Integration Runtime (IR) is the compute infrastructure used by the Data Factory
to provide data integration capabilities across different network environments.
Azure Integration Runtime can be used to connect to data stores and compute services in public networks with publicly
accessible endpoints. Use a self-hosted Integration Runtime for
private/on-premises networks.
There are two options to connect
now.
- Connection String: In connection string
also, there are two options for account selection method
- Account Selection method: Select from a
list of available Azure SQL servers and databases in your Azure subscriptions
or enter server name and database name manually.
- From
Azure Subscription: Enter the details manually.
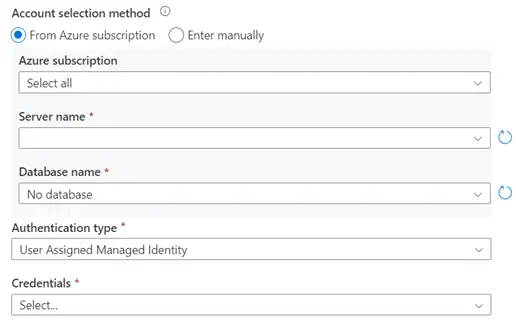
- Azure Subscription: All the subscription
will be listed in the dropdown; you need to choose the appropriate one.
- Server name: Enter your server name.
- Database name: find this out from the
Azure SQL DB connection string.
- Authentication type: there are four types
of authentication types, choose one and accordingly enter the details.
- SQL Authentication: If you know the ID
and Password, you can choose SQL Authentication.
- System Assigned Managed Identity: Grant
Data Factory service managed identity access to your Azure SQL Database
- Service Principal: For this
authentication, along with general properties you need to specify a few things
like, ServicePrincipalId, ServicePrincipalKey, tenant. For more details, refer
this.
- User Assigned Managed Identity: You need
to provide credentials for this type of identity. Reference.
- Enter
Manually: Enter all the details below manually.
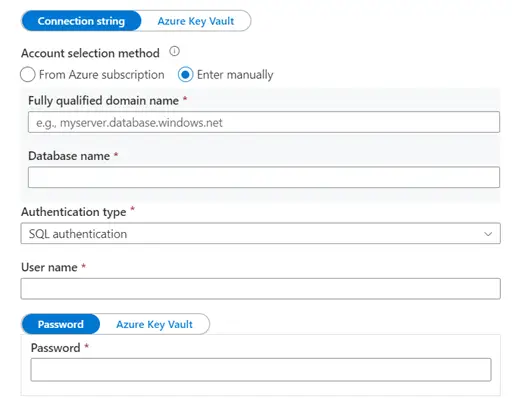
- Fully qualified domain name: You can see
this value from your Azure SQL Database connection string.
- Database name: Again, refer the
connection string
- Authentication type: There are a few
options here.
- SQL Authentication: If you know the ID
and Password, you can choose SQL Authentication.
- System Assigned Managed Identity: Grant
Data Factory service managed identity access to your Azure SQL Database
- Service Principal: For this
authentication, along with general properties you need to specify a few things
like, ServicePrincipalId, ServicePrincipalKey, tenant. For more details, refer
this.
- User Assigned Managed Identity: You need
to provide credentials for this type of identity. Reference.
- After all the details are added you can test the
connection from the bottom right corner of the screen.
 .
.
Example 2: How
to create an ADF Linked service to SharePoint Library?
- Now search for SharePoint from the list of
databases.

- Enter all the required details.
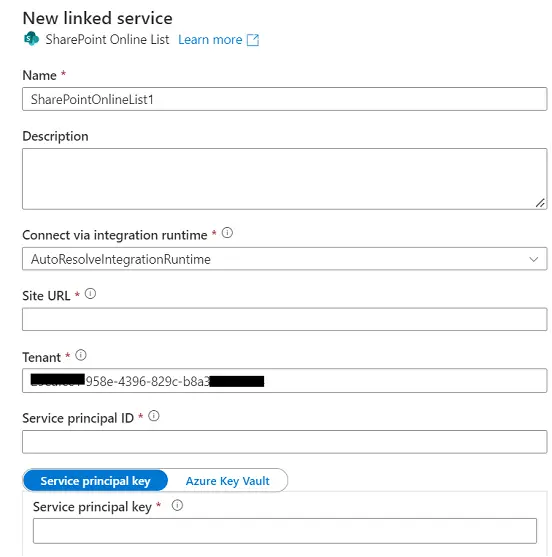
- Name: Enter meaningful name to the Linked
service.
- Description: Describe your linked service
in an understandable manner.
- Site URL: Put the SharePoint Site URL
here.
- Tenant: The tenant ID under which your
application resides. You can find it from Azure portal Active Directory overview
page.
- Service Principal ID: The application
(client) ID of your application registered in Azure Active Directory. Make sure
to grant SharePoint site permission to this application.
- Service
principal key: The client secret of your application registered in Azure
Active Directory.