In this article, we
are going to learn the steps of creating a Data Factory in Azure that can be
done through the Azure Portal.
- Log into Azure Portal: Go to Azure Portal and sign in with your
Azure account credentials.
- Navigate to Azure Data Factory: On the Azure Portal
dashboard, select “Create a resource”. In the search box, type "Data
Factory" and select it from the results.
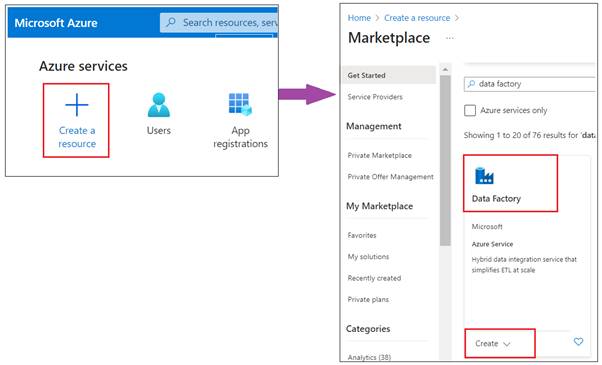
- Initiate Creation: Click on “Create” to
start the process of creating a new Data Factory.
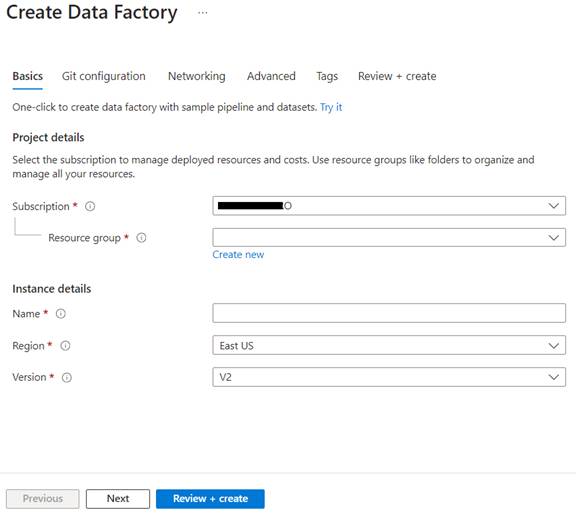
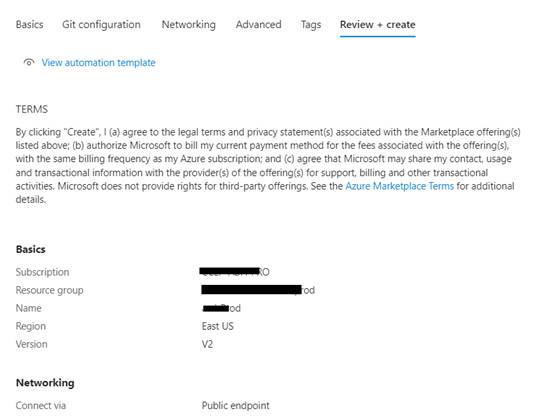
- Fill in the Basic
Details:
- Subscription: Select the Azure
subscription in which you want to create the Data Factory.
- Resource Group: Choose an existing
resource group or create a new one. A resource group is a container that holds
related resources for an Azure solution.
- Name: Enter a globally unique name for your
Data Factory.
- Version: Choose V2, as it's
the latest version with more features and capabilities.
- Region: Select the region closest to your
users or where your data resides to minimize latency.
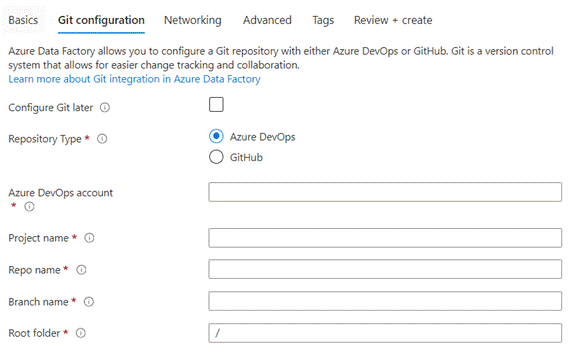
- Git Configuration: Optionally, you can
configure Git for source control. This step allows you to associate your Data
Factory with a Git repository for version control, collaboration, and
development lifecycle management.
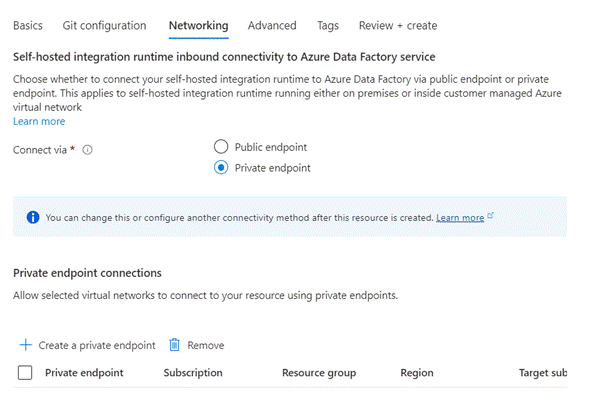
- Networking: You can also
configure networking settings for your Data Factory, such as setting up a
private endpoint for secure connectivity.
- Review: Check all the details you've entered.
Make sure everything is correct as per your requirements.
- Create: Click the “Create” button. Azure will
then validate your configuration and deploy a new Data Factory instance.
- Access and Use the
Data Factory
- Navigate to Your Data
Factory:
Once the deployment is complete, go to the newly created Data Factory resource.
- Open ADF Studio: To start using Data
Factory, click on the “Author & Monitor” button in the Data Factory
overview page. This will open the Azure Data Factory Studio, where you can
create and manage pipelines, datasets, linked services, and more.
- Best Practices
- Naming Conventions: Use clear and
consistent naming conventions for ease of management, especially if you will
have multiple Data Factories.
- Resource Organization: Keep your Data
Factory within a relevant resource group along with related Azure resources for
better organization and management.
- Security and
Compliance:
Consider implementing security measures like managed identities, Azure
role-based access control (RBAC), and ensuring compliance with your
organization's policies.